Content Delivery Network (CDN) affects your online life more than you suspect. You can appreciate its impact when loading any content on the site and applications: audio, video, streaming, images, texts, graphics. CDN helps to quickly deliver content to the user, which is important in many areas. For example, due to a long loading page of an online store, the customer will go to competitors, and if the media site loads for a long time, then the reader will choose another online media.
In this article, we will discuss the CDN device and its importance for businesses and users, together with ITGLOBAL.COM experts.
What is a CDN
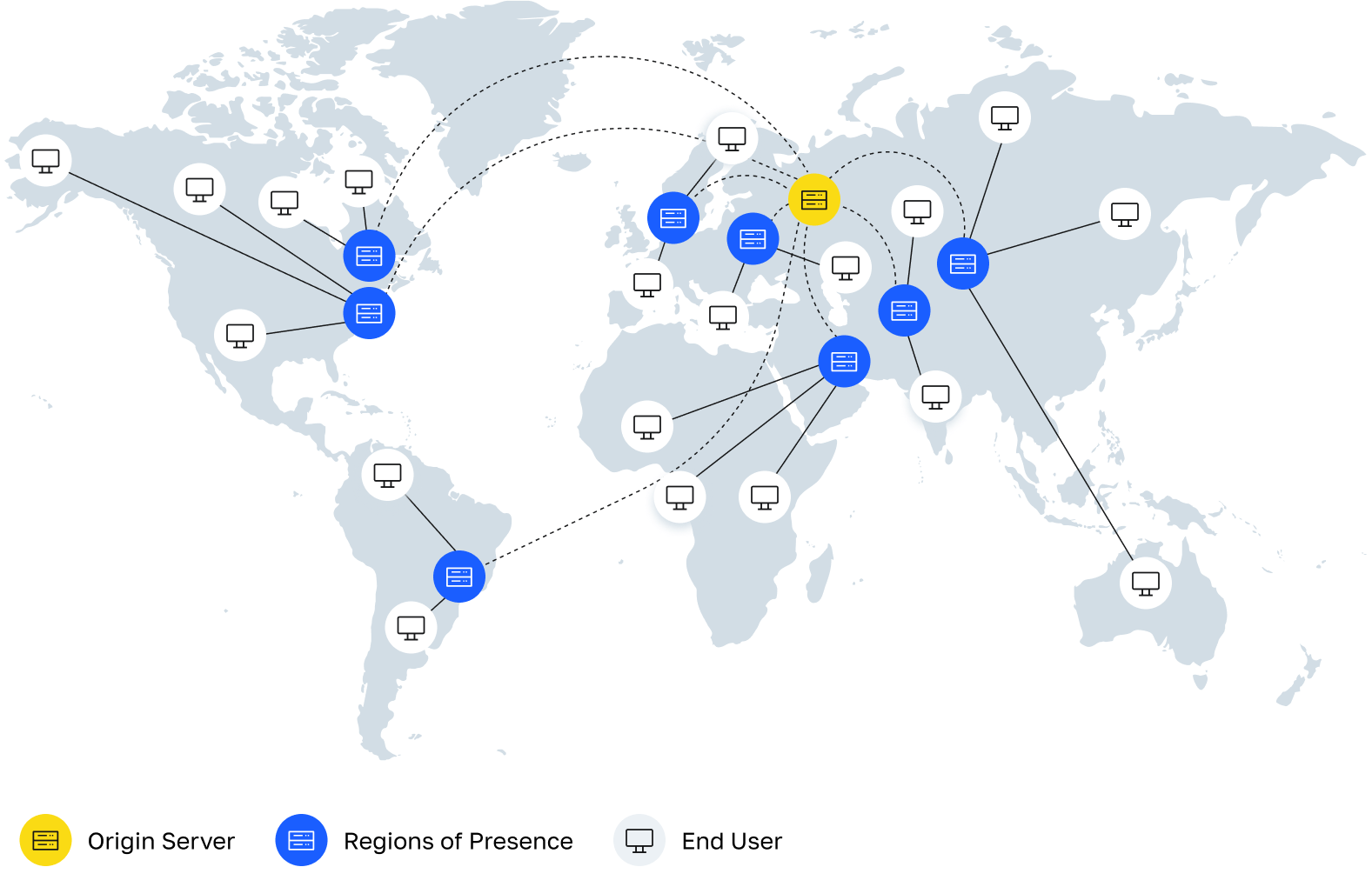
CDN is a distributed network architecture created to speed up the delivery of content to users. In conventional hosting, the client requests content from the server that stores the data. The server processes the request and transmits a data packet, after which the website or application is loaded. CDN hosting includes additional servers in the chain that are responsible for caching content.
The content delivery network has its own servers in the maximum number of geographical locations. Due to the distributed network of CDN servers, the distance between the original server and the user does not affect the speed of data transmission.
The history of CDN
Akamai launched the first CDN in 1998, whose methods serve as the basis for modern content delivery networks. The first-generation CDNs were focused on static content: software, images, archives.
As cloud and mobile computing spread, second-generation CDN services developed. They provided efficient delivery of more complex dynamic multimedia and web content. With the growing number of internet users, the number of CDN providers and the services they offer increased.
Some CDN business models are based on the volume of content delivered. Other providers offer basic services for a fixed fee or even for free, charging additional fees for performance improvements and optimization.
CDN operation principles
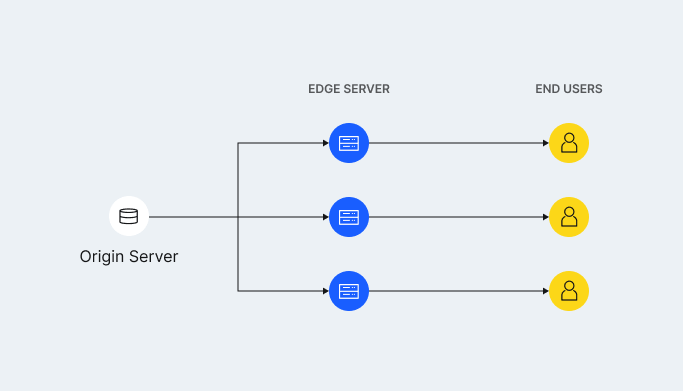
The CDN architecture includes:
- Source server – stores the source data that is retrieved by edge nodes. The source server is a cloud storage or a dedicated server. A CDN can include several such servers;
- Edge node, or Presence point (or PoP) – a geographically distributed local server that delivers cached content to users.
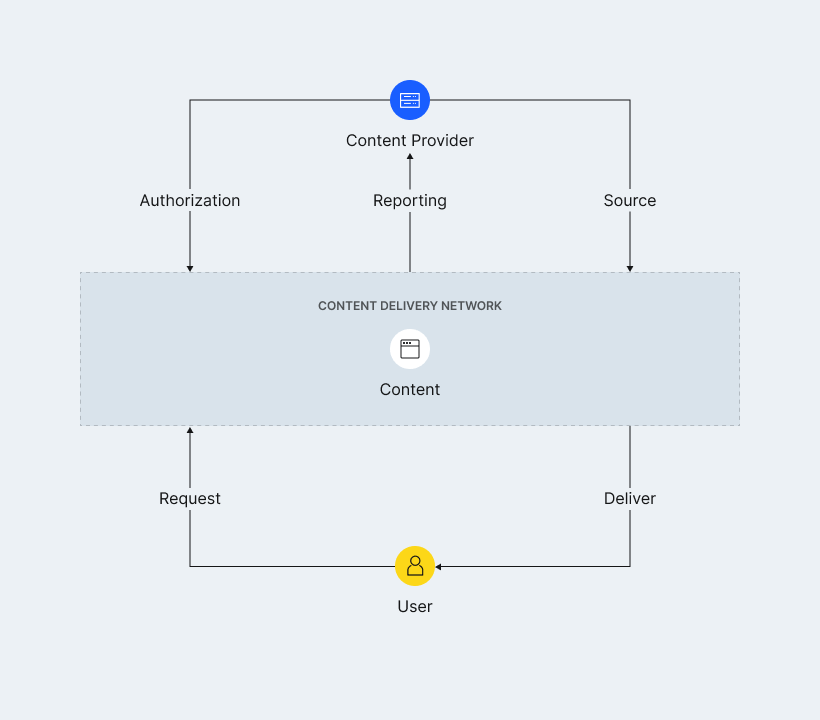
Content hosted on the source server is duplicated at the presence points. When a user visits the site, the content is loaded from the nearest intermediate node. In the absence of a CDN, site visitors request information and receive responses directly from the primary source. This method increases the requirements for the source server, as each request increases the load, and the user’s distance from the source increases the page loading time.
An edge node is the main component of a CDN. It stores copies or cached versions of website content received from the origin server, and it provides content on demand. Caching servers act as reverse proxy servers, which are connection points located in front of web servers and act as intermediaries for end-user requests. Reverse proxy servers intercept requests, forward them to web servers, and return responses to website visitors.
In addition, origin shields can be added to the CDN architecture. They also function as a reverse proxy and protect the origin server from overloads.

The main function of the screening server is to offload the source server from traffic spikes, it proxies requests, adding another layer of protection.
CDN mechanisms
There are several mechanisms that make a CDN work:
- caching rule – determines how long content remains in the cache at the edge level;
- time to live (TTL) – the time period of caching at the edge node before a new data retrieval from the source server;
- clearing – the mechanism and process of clearing content at points of presence;
- limitation – a rule that regulates access to content from the cache, for example, allowing requests only from certain geographic or domain zones.
Content types
The content processed by the CDN is divided into two types:
- Static content is files on the server that do not change during the download: HTML files, images, videos.
- Dynamic content is data that changes depending on the user. Dynamic content is affected by gender, browsing history, session time, location, user device, and other factors. Dynamic data is generated by scripts that change the content of a web page. The same website will look different for different users, making it more personalized and interactive. A prime example is social media feeds t which adapt to user activity such as likes, comments, and shares.
Static and dynamic content places different demands on servers. Static content uses RAM, while dynamic content relies on network speed. Both types of content place a double burden on a single server.
CDN tools
To understand where the nearest edge node is located and to correctly direct the user, there are two CDN tools:
- GeoDNS – based on the algorithm of converting an IP address to geocoordinates. After the request arrived, the DNS server determines the location of the user by IP address and finds the nearest point of presence.
- Anycast – works with the BGP protocol, which transmits information about neighboring networks and the distance to them. In terms of functions, Anycast is similar to GeoDNS.
Get a consultation on CDN
What problems a CDN solves
Performance and latency reduction
There are many factors that affect the performance of a website or application, such as DNS and host server settings, code quality and optimization, and the distance between the web server and the user’s location. A CDN solves this problem.
 The response time for content hosted on a CDN network is significantly lower than the response time (download time) for content accessed directly from the content generator’s website. A CDN allows content to be downloaded instantly, regardless of the location of the source server. For example, a user may be in Belgrade while the server is in Bangkok. CDN servers allow more simultaneous visitors from different countries to access the website.
The response time for content hosted on a CDN network is significantly lower than the response time (download time) for content accessed directly from the content generator’s website. A CDN allows content to be downloaded instantly, regardless of the location of the source server. For example, a user may be in Belgrade while the server is in Bangkok. CDN servers allow more simultaneous visitors from different countries to access the website.
Load distribution and scalability
A CDN helps distribute the load on servers and protects users from traffic spikes. The computing resources and bandwidth of the origin server are limited, and if the number of client requests exceeds what the server can handle, the website or application may become unavailable.
By using caching servers, bandwidth consumption on the origin server is reduced, helping to preserve network resources and improve overall performance.
Load balancing
If there are multiple origin servers in the architecture, the CDN acts as a load balancing tool, distributing incoming requests. This helps to manage traffic congestion and optimize server capacity.
DDoS protection and infrastructure security
CDN improves infrastructure security. It is expensive and difficult to maintain local solutions for DDoS attacks. CDN servers are distributed across continents and provide a wide bandwidth, which means that a DDoS attack on a website will be distributed across multiple servers. Many CDNs also use additional filtering and security mechanisms that improve and enhance their strategies for protecting against cyberattacks.
Web application security
A content delivery network increases application security. A CDN can be equipped with a WAF (Web Application Firewall). This tool is designed to protect applications from vulnerabilities by blocking cyberattacks and common exploits.
Traffic encryption
CDN provides traffic encryption. Using SSL/TLS encryption increases security. CDN encrypts traffic when it passes through edge servers, which is especially important if the site does not have its own SSL certificate.
Who needs a CDN
A local online store or a website with light statistics will probably not need a CDN for optimization. For companies that work with a lot of data, especially dynamic content, a CDN can help them build and maintain an audience.
Typically, a dynamic content network is used by:
- large online stores with a distributed audience and peak loads;
- streaming services with streaming of audio and video content;
- companies that actively use mobile applications;
- gaming portals: distributors and providers of cloud gaming services.
Conclusion
CDN increases the speed of loading websites and applications. This factor is key for all users. For a company that works for a wide audience, CDN will help to provide high-quality services and promote their goods, but it is important to choose a provider that can meet all the requirements of a high-quality CDN.
ITGLOBAL.COM hosts CDN servers in 8 countries: the Netherlands, the USA, Canada, Brazil, the UAE, Russia, Kazakhstan. When using a CDN, the web server response time rarely exceeds 10 ms, which allows for the fastest possible delivery of content to all internet users. A CDN is an essential part of the infrastructure for any project with a large audience.
Get a consultation on CDN